Ugo Basile’s Contribution to Preclinical Research: Advancing Solutions for Schizophrenia

Ugo Basile’s Contribution to Preclinical Research: Advancing Solutions for Schizophrenia
24th May marks the World Awarness Day on Schizophrenia, a chronic and severe mental disorder that affects around 24 million people worldwide. It usually begins in late adolescence or early adulthood, and its impact can be profound and long-lasting, affecting many aspects of a person’s life.
The World Health Organization (WHO) notes that individuals with schizophrenia are 2 to 3 times more likely to die early compared to the general population. This is often due to preventable physical health conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and infections, which may go undiagnosed or untreated.
Advancements in understanding and treating schizophrenia heavily rely on preclinical research using animal models. Preclinical studies focus on replicating schizophrenia-like symptoms in animals, such as cognitive deficits, social withdrawal, and sensory processing anomalies, to explore disease mechanisms and evaluate the efficacy of new treatments.
Ugo Basile offers a range of sophisticated tools designed to facilitate preclinical studies on schizophrenia.
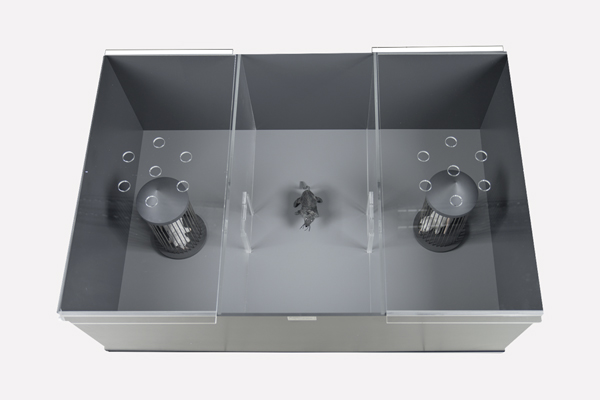
OPERON Dual Chamber System
Cognitive flexibility impairments are a hallmark of schizophrenia.
The OPERON Dual Chamber is a fully automated system designed to assess executive functions in rodents through tasks analogous to the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST) and the CANTAB Intra-/Extra-Dimensional set-shifting task (ID/ED used in humans. It evaluates cognitive flexibility by requiring subjects to shift attention between different stimuli dimensions (e.g., visual, olfactory, tactile).
Lear more about Operon by Ugo Basile: https://ugobasile.com/products/categories/behaviour-conditioning-reward/operon-papaleo-scheggia-s-method
The Scarsi et al. paper “Automated Two-chamber Operon ID/ED Task for Mice” (2020, Current Protocols) provides a detailed step-by-step protocol for preparing and testing mice that includes all procedures required for this upgraded attentional set-shifting paradigm. All OPERON systems are provided with customizable procedures for 2 or 3 dimensional tests using a dedicated version of the highly cited ANY-maze software. Tools for adapting protocols to the different experimental needs are also included and easy to tweak in a graphical way with no coding needed.
In the 2023 paper "Automation at the service of the study of executive functions in preclinical models” published in Scientific Reports, a detailed examination of how the OPERON automated system is revolutionizing research of Attentional Set-Shifting and, more in general, Brain Executive Functions.
A number of considerations were drawn about the advantages and disadvantages of using a fully automated method through the OPERON:
- Lower level of operator training
- Higher degree of standardization
- Protection from operator mistakes (e.g. common inversion of rewarded stimuli)
- Elimination of experimenter-driven variability and bias
The paper also highlights several key applications of the OPERON system in the study of executive functions relevant to schizophrenia, including:
- Impulsivity and attentional processesare studied thanks to the automated nature of the OPERON, allowing for precise control over stimul presentation and response measurement.
- Reversal Learning Tasksmeasure cognitive flexibility by requiring animals to adapt to changing reinforcement contingencies or, in other terms, task rule changes. The OPERON's ability to automate these tasks ensures that researchers can systematically investigate how schizophrenia affects the ability to adjust to new rules across changing stilmuli and environments/dimensions.
In summary, the automation provided by the OPERON offers several significant advantages for schizophrenia research in rodents (mice):
- Enhanced Accuracy: by minimizing human intervention, the OPERON reduces the risk of errors, increases the precision of behavioral measurements and optimizes experiment reliability.
- Increased Throughput: the ability to run a number of increasingly complex tasks and continuously collect data, accelerates the research process by maximizing the ability of animals to perform subsequent tasks. This high-throughput capability is essential for large-scale studies and drug screening.
- Reproducibility: Automated systems ensure that experimental conditions are standardized across trials and subjects, enhancing the reproducibility of results. This is critical for validating findings and translating them into clinical considerations.
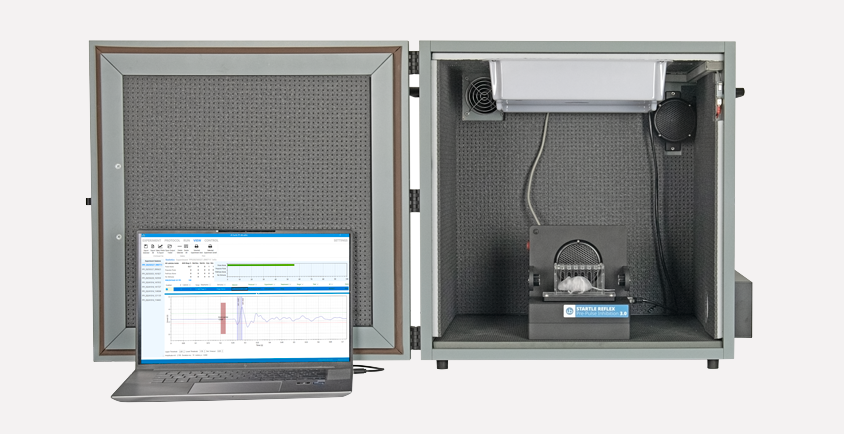
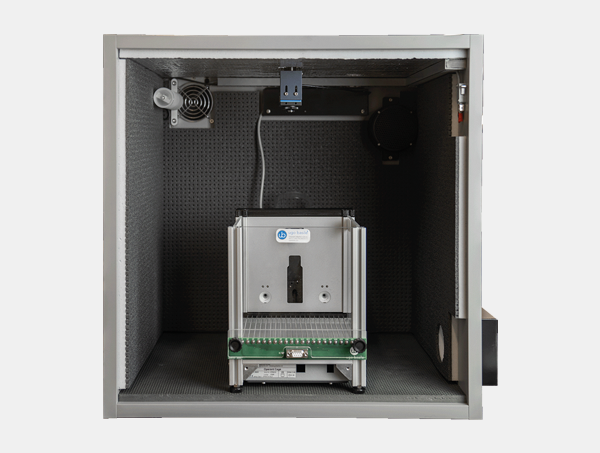
Startle Reflex and Pre-Pulse Inhibition (PPI) Test
Startle Prepulse Inhibition (PPI) is an experimental paradigm commonly used in rodents, such as mice and rats, to study sensorimotor gating, which refers to the brain's ability to filter out irrelevant sensory stimuli and prevent them from overwhelming the processing of more important stimuli. Sensorimotor gating refers to the ability of a sensory event to suppress or decrease a motor response, in this case, a startle response.
The Startle PPI paradigm has been widely used in neuroscience research to study sensorimotor gating deficits induced by pharmacological agents and to evaluate the effects of potential therapeutic interventions for disorders like schizophrenia, where PPI deficits are often observed.
The new 2025 version of Startle/PPI system by Ugo Basile has been recently upgraded to provide enhanced precision, flexibility, and ease of use. The main improvements include:
- Easy Platform Calibration: The sensitivity and offset of the load cell can now be calibrated directly via firmware/software, without manual intervention. Each system comes with a platform calibrator, allowing users to standardize sensitivity across multiple cubicles, depending on the animal’s weight and the type of restrainer used.
- Sound Calibration Flexibility: The new systems allow sound levels to be calibrated without user intervention on the electronic board.
- Simplified Connection Between PPI and Fear Conditioning Modules: Thanks to the new CBOARD01 board, speakers for different modules are managed independently. No manual unplugging is needed. Switching from PPI to FC now only requires connecting one cable.
- Optimized Auxiliary TTL Signals: The AUX1 (linked to stimuli) and AUX2 (for environmental controls) signals are now accessible via an optional TTL I/O Interface, offering a cleaner and more customizable setup tailored to the experimental protocol.
The latest software version includes:
- Calibration of load cell sensitivity directly via firmware/software
- Fine-tuning of response thresholds.
- Resizable graph in the VIEW page.
- User-defined cubicle numbering (1, 2, 3, or 4), no longer dependent on the operating system.
Learn more about NEW Startle/PPI System by Ugo Basile: https://ugobasile.com/download/Behaviour%20Conditioning/Startle%20PPI/48000_Startle-PPI_Brochure_Rev2-2_202504_web.pdf
Operant Fear Conditioning
The Operant Fear Conditioning (OFC) is a dual-purpose systems to be used for Operant or Fear Conditioning experiments.
A standard Fear Conditioning cage has been modified adding an operant wall with 1 pellet dispenser, 2 nose pokes, a house light and 2 cue lights above the nose pokes. The operant wall can be hidden by a removable plastic wall to use the cage as a standard Fear Conditioning.
Operant experiments are fully programmable with the ANY-Maze software, with protocols ranging from Fixed or Variable Ratio, Fixed or Variable Schedule, Progressive Schedule, Delay Discounting, Extinction, etc.
At the same time, the operant wall can be covered and standard Cued and Contextual Fear Conditioning experiments can be performed with high freezing detection performance, thanks to the ANY-Maze software.
The Operant Wall and the Fear Conditioning set-up can also be used in combination for Avoidance Experiments, for example by partially covering the grid floor with a small plastic platform and measuring the motivation of rodents to leave the platform and get the pellet, in spite of the shock risk (Bravo-Rivera et al., 2014, The Journal of Neuroscience).
Since Schizophrenia is characterized by impairments in associative learning, emotional regulation, and cognitive flexibility, the OFC system facilitates the exploration of these deficits through:
- Fear Conditioning Paradigms: Assessing the acquisition and extinction of conditioned fear responses, which are often disrupted in individuals with schizophrenia.
- Operant Tasks: Evaluating decision-making processes, reward sensitivity, and behavioral flexibility, providing insights into the cognitive dysfunctions associated with the disorder.
Learn more on Operant Fear Conditioning by Ugo Basile https://ugobasile.com/products/categories/behaviour-conditioning-reward/operant-fear-conditioning-ofc
Five-Hole Choice Serial Reaction Time Task (5-CSRTT)
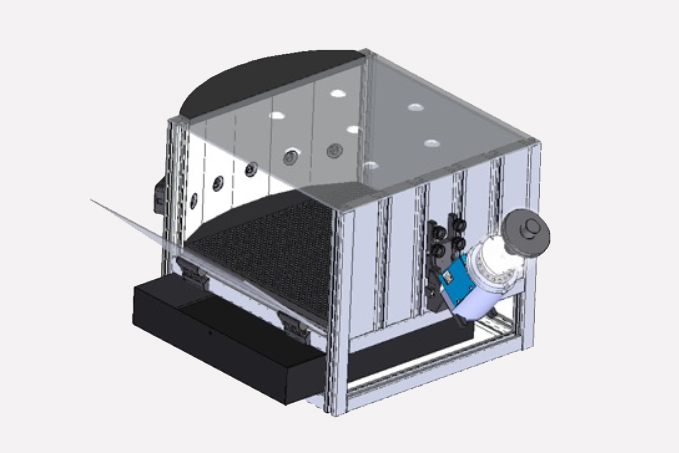
The primary goal of the 5-CSRTT is to measure an animal’s ability to sustain attention and make rapid, accurate decisions in response to visual cues. The rodent is trained to associate the appearance of a cue in a specific port with a reward, typically a food pellet or a drop of liquid. The animal’s task is to quickly and accurately identify the port where the cue appeared and make a nose-poke response in that port to receive the reward. Researchers collect data on various parameters, including response accuracy, response latency, omission errors, and premature responses.
Overall, the 5-choice serial reaction time task is a versatile and widely applied tool in behavioral neuroscience, helping researchers gaining a better understanding of the neural and behavioral mechanisms underlying a range of cognitive processes and their relevance to various health and disease conditions, mainly related to attention and impulsivity, such as ADHD, schizophrenia, addiction, etc.
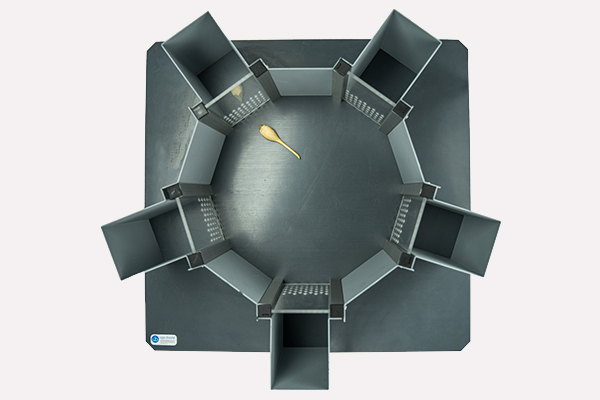
AGORA Maze (SocioBox Method)
The AGORA Maze, inspired by the SocioBox paradigm, is a behavioral test designed to assess complex social recognition in mice. The system consists of a central open arena surrounded by five peripheral compartments, each housing a stimulus animal (familiar, unfamiliar, dominant, or of a different gender). The subject mouse moves freely within the central area, and its social preference is measured based on the time spent near each stimulus chamber.
The AGORA Maze is primarily used for research in social behavior and recognition memory in rodents. It provides a powerful tool for assessing deficits in social cognition, which are characteristic of various psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s.
The study Krueger-Burg et al. (2016) “The SocioBox: A Novel Paradigm to Assess Complex Social Recognition in Male Mice” (Krueger-Burg et al. (2016) Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience) introduced the SocioBox paradigm validating the system’s ability to detect a subject mouse’s ability to distinguish a novel mouse among five conspecifics, providing a robust platform for investigating social deficits relevant to psychiatric disorders like schizophrenia and autism.
Read the complete open access paper: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00145/full
Learn more on Agora Maze Sociobox Method by Ugo Basile https://ugobasile.com/products/categories/mazes-tracking/agora-maze-sociobox-method
Three-Chamber Sociability Test
Social behavior in rodents is gaining growing attention in neuroscience and behavioral pharmacology, especially as researchers increasingly recognize the limitations of conducting experiments on isolated animals. Despite being naturally social creatures, mice and rats have often been studied under conditions that ignore their intrinsic social dynamics. This shift in perspective has highlighted the need for reliable, reproducible tools to study social interaction and memory.
The Three-Chamber Sociability Test, first introduced by J. Crawley in 2004, has become a classic method to investigate sociability and preference for social novelty key aspects of rodent social behavior. Originally developed to model core symptoms of autism spectrum disorders, the test is now widely applied in neuropsychiatric research, including schizophrenia, as well as in transgenic studies and pharmacological screening.
The test setup involves a central arena divided into three chambers. A single test animal is allowed to move freely between the compartments, while two stimulus animals are confined in grid bar enclosures located in the side chambers. By measuring the amount of time the subject spends near each enclosure, one exposing the free animal to a stranger and to a cage-mate to assess the subject’s preference for social novelty.
Compatible with ANY-maze software, the system supports high-throughput behavioral analysis and is ideal for use in complex, multi-subject experimental designs.
In schizophrenia models, reduced social novelty preference has been observed, mirroring symptoms of social withdrawal and impaired social cognition seen in patients. It also supports studies comparing gender differences, strain variability, and other behavioral phenotypes.
Learn more on 3-chamber Sociability Test by Ugo Basile https://ugobasile.com/products/categories/behaviour-conditioning-reward/operant-fear-conditioning-ofc
For more information on Ugo Basile's instruments and their applications in neuroscience research, please visit Ugo Basile's official website.