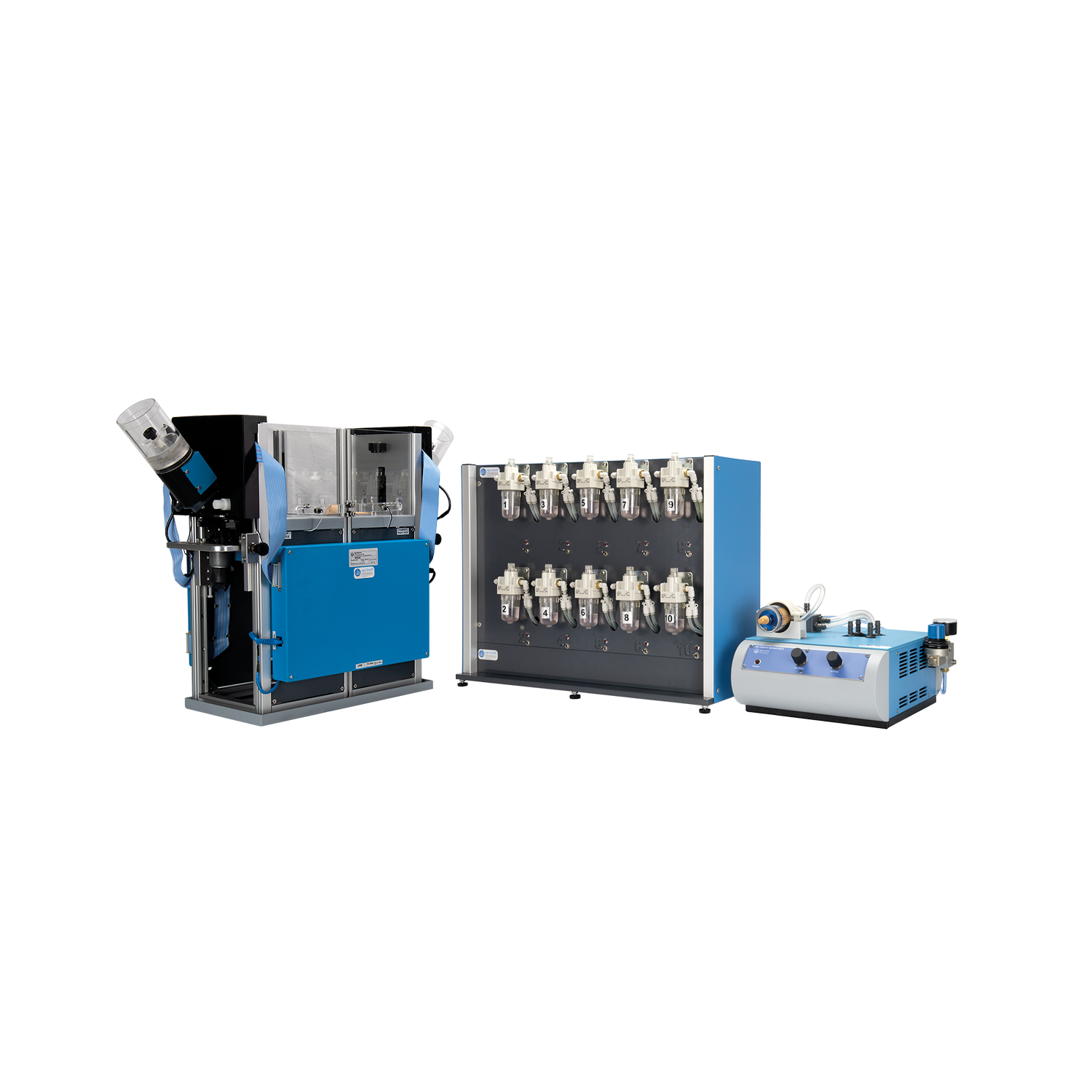
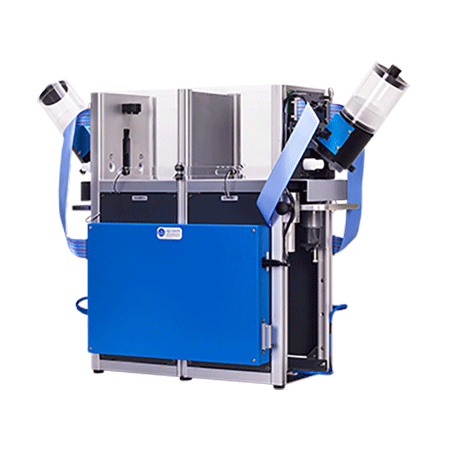
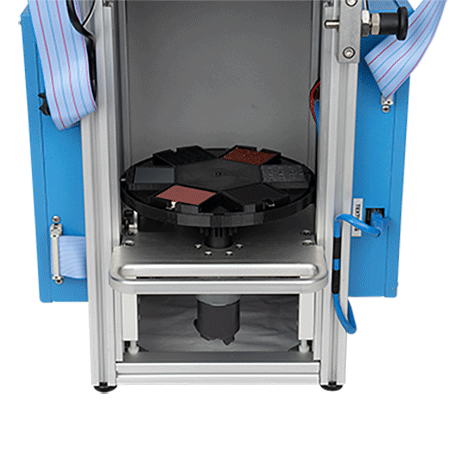
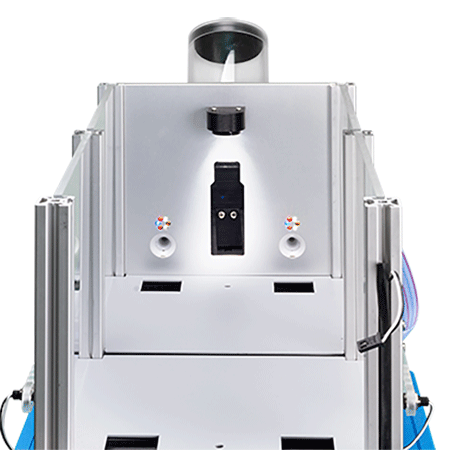
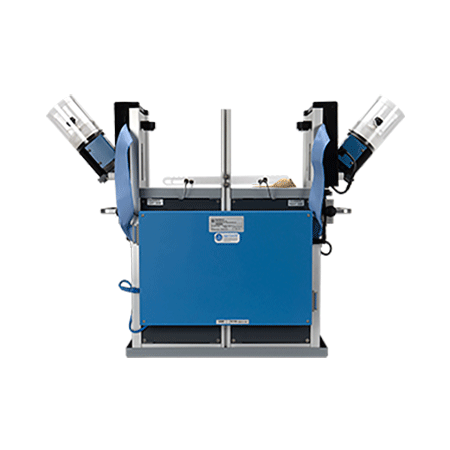
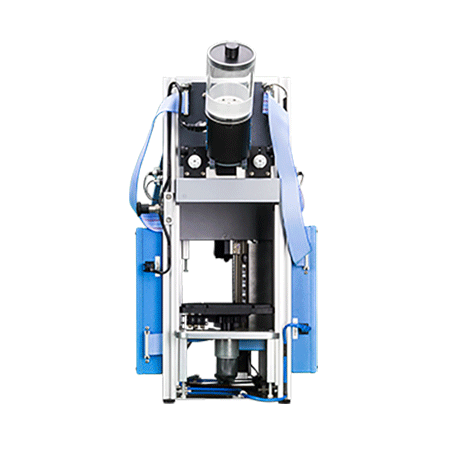
Optional Extended Warranty (UB Care)
In addition to the one-year Regular Warranty and in addition to the one-year product registration extended warranty, Ugo Basile offers an Optional Extended Warranty that extends the warranty period for the product for additional one or two years called “UB Care12”/“UB Care24”. Customers may purchase the “UB Care” at the maximum of 3 months after buying. For more detailed information, please contact your local representatives.