G. Amodeo, G. Galimberti, P. Sacerdote, S. Franchi, 2023, "Characterization of prokineticin system in Crohn's disease pathophysiology and pain, and its modulation by alcohol abuse: A preclinical study", Elsevier Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease
K. A.El-Saiy, R.H. Sayed, A. E. El-Sahar, E. A. Kandil, 2022, "Modulation of histone deacetylase, the ubiquitin proteasome system, and autophagy underlies the neuroprotective effects of venlafaxine in a rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease model in rats", Elsevier
C. P. Papaneophytou, E. Georgiou, C. Karaiskos, I. Sargiannidou, K. Markoullis, M. M. Freidin, C. K. Abrams, K. A. Kleopa, 2018, "Regulatory role of oligodendrocyte gap junctions in inflammatory demyelination", GLIA
E. El-Horany, R. N. Abd El-latif, M. M. ElBatsh, M. N. Emam, 2016, "Ameliorative Effect of Quercetin on Neurochemical and Behavioral Deficits in Rotenone Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease: Modulating Autophagy (Quercetin on Experimental Parkinson's Disease)", Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology
J. Ajarem, N. G. Altoom, A. A. Allam, S. N. Maodaa, M. A. Abdel- Maksoud, B. KC. Chow , 2016, "Oral administration of potassium bromate induces neurobehavioral changes, alters cerebral neurotransmitters level and impairs brain tissue of swiss mice", Elsevier
L. Liu, C. Peritore, J. Ginsberg, J. Shih, S. Arun, G. Donmez, 2015, "Protective role of SIRT5 against motor deficit and dopaminergic degeneration in MPTP-induced mice model of Parkinson's disease", Elsevier
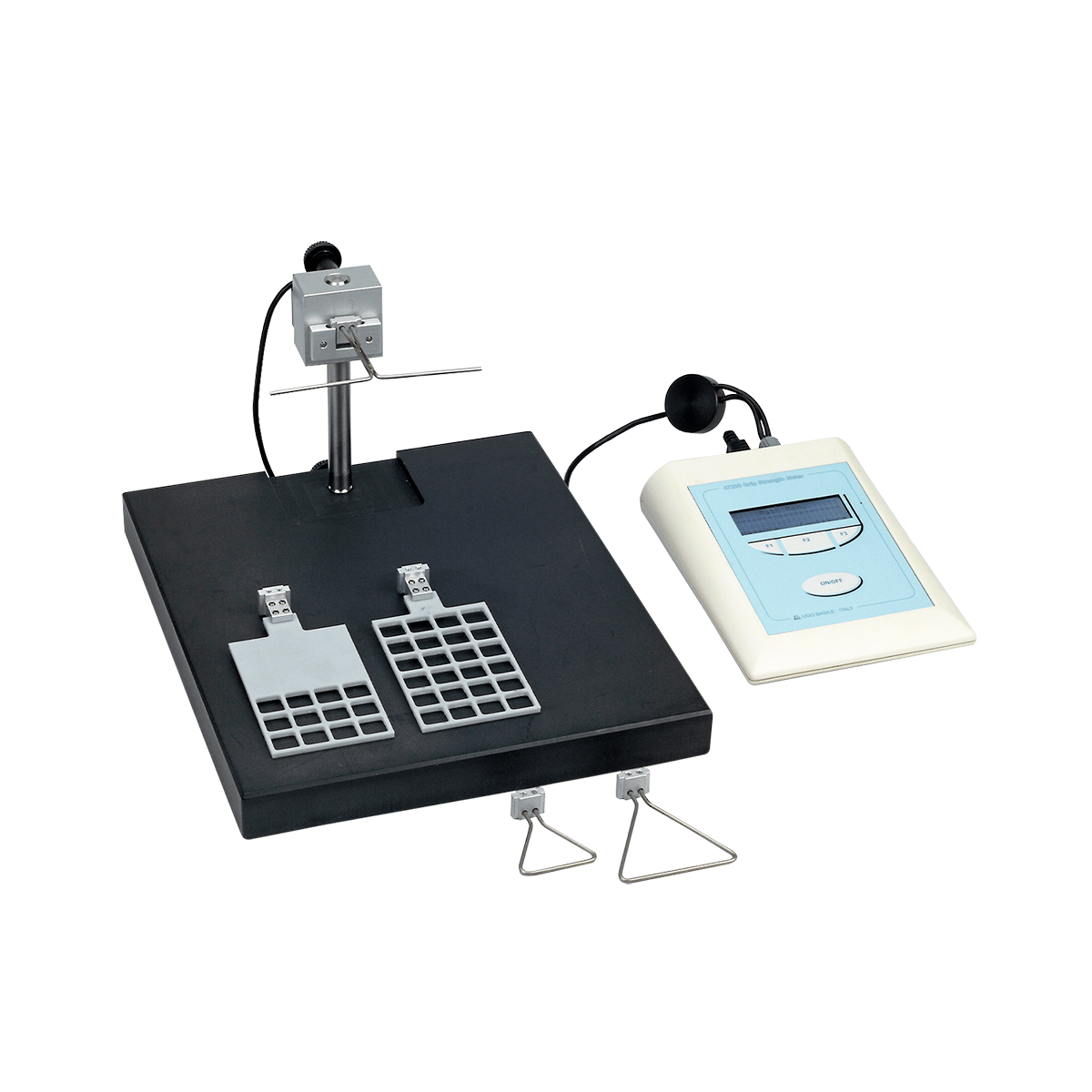
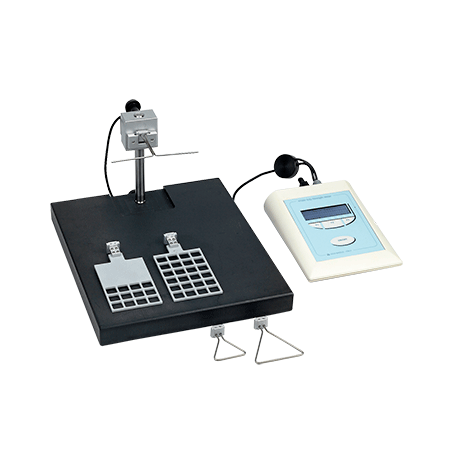
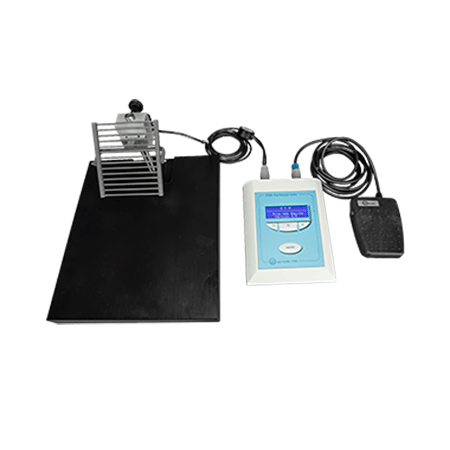
J. B. Stephenson IV, R. Li, J. Yan, J. Hyde, H. Matloub, 2013, "Transhemispheric Cortical Plasticity Following Contralateral C7 Nerve Transfer: A Rat Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Survival Study", Elsevier
F. Richter, M. Hamann, A. Richter, 2006, "Chronic rotenone treatment induces behavioral effects but no pathological signs of parkinsonism in mice", Journal of Neuroscience Research
P. Dion, V. Shanmugan, C. Gaspar, C. Messaed, I. Meijer, A. Toulouse, J. Laganiere, J. Roussel, D. Rochefort, S. Laganiere, C. Allen, G. Karpati, J. Bouchard, B. Brais, G. A. Rouleau, 2005, "Transgenic expression of an expanded (GCG)13 repeat PABPN1 leads to weakness and coordination defects in mice", Elsevier